 |
|
NASA PODAAC Multiscale Ultrahigh Resolution (MUR) |
|
NASA's Physical Oceanography Distributed Active Archive Center (PODAAC) generates the Multiscale Ultrahigh Resolution sea surface temperature (SST) product (version 4.1) that combines data from all current microwave and infrared polar-orbiting and geostationary satellites, including U.S. satellites and those of international partners such as Japan and Europe. The satellite instruments vary on a daily basis depending on availability, but may include the following, among others:
Nighttime skin and subskin SST observations from the available satellite instruments are blended (analyzed) using an optimal interpolation approach, called multi-resolution variational analysis (MRVA). The analysis technique includes in-situ SST observations from the NOAA iQuam project. As with data assimilation approaches, the in-situ SST observations are used in a bias correction to "nudge" the satellite SST's in the direction of the in-situ SST's for a more accurate analysis product. The number of included satellite instruments, and the analysis technique, allows for a daily, cloud-free, global product on a 0.01 degree grid (approximately 1 km). The multi-resolution variational analysis method is based on wavelet decomposition. Its multi-scale design allows interpolation of the satellite pixel data at an optimal resolution for each data set, which is particularly useful for combining data sets from sensors with drastically different resolutions. Near real-time SST data are generated by PODAAC with a 2-day delay, and retrospective science-quality SST data are generated with a 4-day delay. NOAA CoastWatch East Coast Node obtains the retrospective science-quality data and subsets it for the contiguous United States (CONUS) coasts. In addition to daily files, monthly and annual mean composite files are available. East Coast Node distributes the MUR SST daily, monthly and annual data for the time period 2007 to the present (shorter than PODAAC's 2002 start date), due to the results of a validation study conducted by East Coast Node. 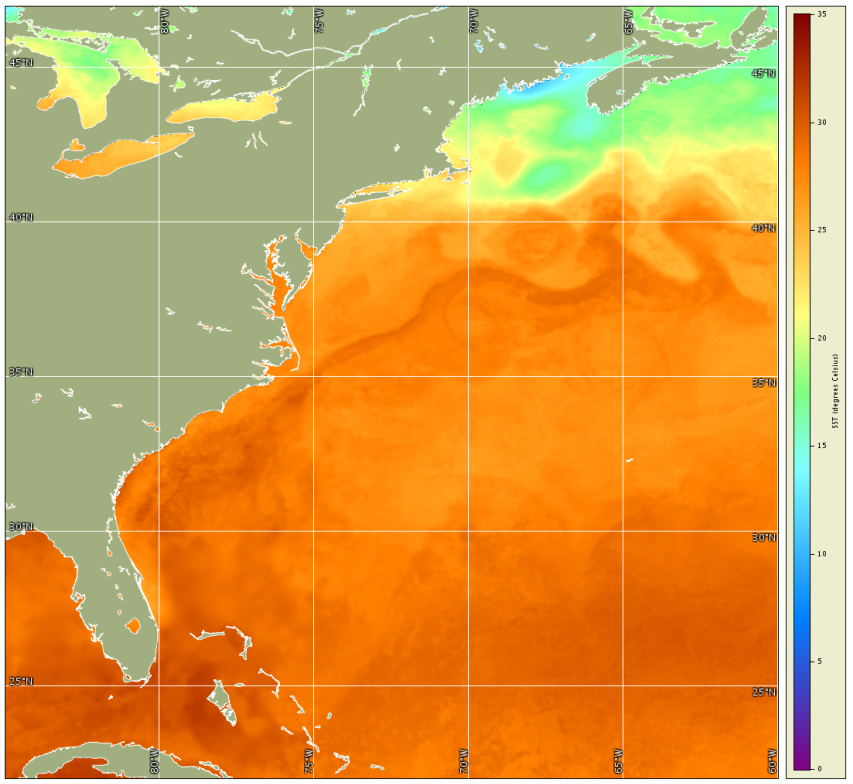
Figure: PODAAC MUR SST for July 30, 2015 Validation of MUR SST was conducted by East Coast Node for Chesapeake Bay. The Multiscale Ultrahigh Resolution SST project is funded by the NASA MEaSUREs Program. More information may be found at the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory MUR project page. References:Chin, T.M., Vazquez-Cuervo, J., and Armstrong, E.M. 2017. A multi-scale high-resolution analysis of global sea surface temperature. Remote Sensing of Environment, vol. 200, pp. 154-169, Oct 2017. doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.07.029 Chin, T.M., J. Vazquez, and E. Armstrong. 2013. Algorithm Theorectical Basis Document: A multi-scale, high-resolution analysis of global sea surface temperature, Version 1.3. NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Physical Oceanography Distributed Active Archive Center. |
- See the Data Access page for data access options.
- Or use Direct Download to retrieve data files by time-interval and region:
|

